The key crop rotation plan is a more flexible way to rotate your vegetable crops than conventional crop rotation plans. This page explains how the key crop rotation plan works.
Why rotate crops
Planting the same type of vegetable in the same place repeatedly increases the risk of a build-up of pests and pathogens and will deplete trace elements. Rotating the different types of vegetables grown in a given bed will reduce the risk of this.
the problem with standard crop rotation plans
Whatever standard crop rotation plan you are using they all rely on rotating the different types of crops through a series of vegetable beds of the same size. But different vegetables require different amounts of space to grow and mature at different times, which often results in a mismatch of the available space for the type of crops you want to grow. For more information see: The Problems With Crop Rotation Plans.
The key crop rotation plan
The key crop rotation plan involves selecting the crops from each of the four planting groups that take up the biggest area in your vegetable garden (designated as key crops) and rotating them as space becomes available. All other vegetable crops that take up less space being planted in the spaces not planted with your key crops.
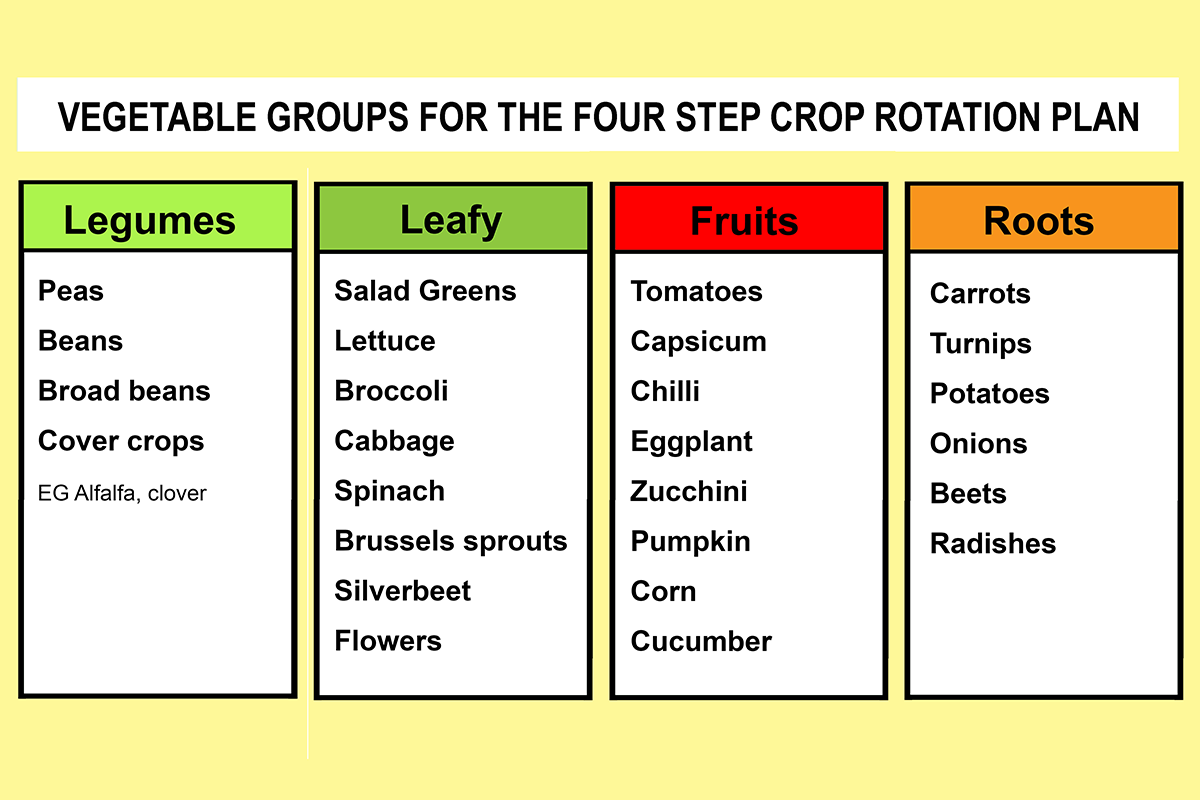
Choose a limited number of crops (no more than three) from each of the four planting groups that take up the biggest area in your vegetable garden, these will be your key crops.
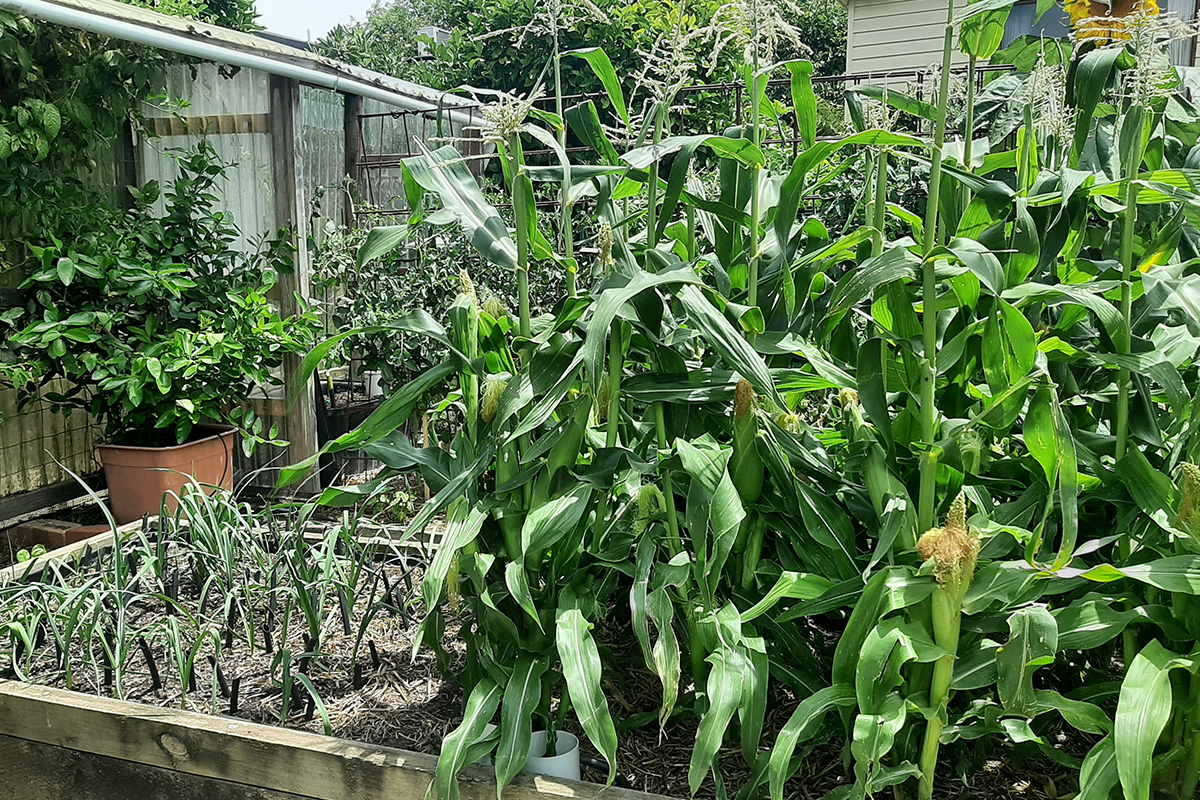

LEFT: Young leek plants. Onions, carrots and leeks are my key root crops, they will be replaced with plants from my key legume crops list, (beans and broad beans). RIGHT: Maturing corn plants(a fruit crop). They will be replaced with my key root crop plants. If there are small or uneven spaces they will be filled with any number of non key crop plants from all the four plant groups, such as lettuces, basil, garlic and celery.
advantages & disadvantages of key crop rotation
The main advantage is that it is more flexible than a conventional crop rotation plan, allowing you to expand into other beds if you need more space for a particular vegetable group. It also means that you can use irregular sized beds, a standard four stage crop rotation plan requires four beds of the same size.
The main disadvantage is that it is more complicated to manage than a standard crop rotation plan as vegetables from a key crop vegetables group may be planted over more than one bed. I get around this by keeping a log of where the various types of vegetables were planted each season. It is also harder to keep to the crop planting sequence of legumes, leafy, vegetables, fruits then root crops in that order. Sometimes you have to plant the same crop type in the same place twice in a row.
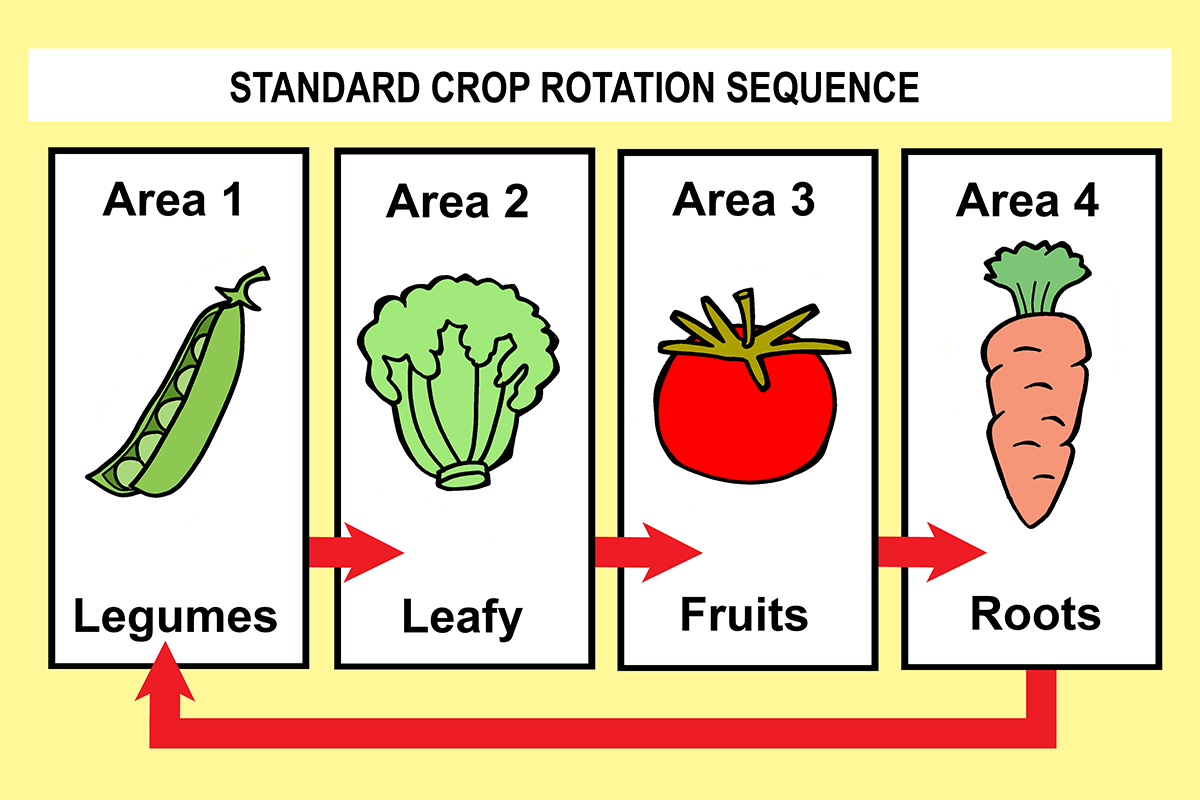
It can be difficult to keep to the crop planting sequence using the Key crop rotation plan.
ADVANTAGES SUMMARY
ADVANTAGES
- More flexible than a conventional crop rotation plan.
- Suitable for use in irregular sized beds.
DISADVANTAGES SUMMARY
DISADVANTAGES
- More complicated to manage than a standard crop rotation plan.
- Harder to keep to the proper crop planting sequence.
- Sometimes you have to plant the same crop type twice in a row.
Key crop rotation summary
The key Crop Rotation Plan is not as reliable as a conventional crop rotation plan as there will be times that you cannot follow the proper vegetable group planting sequence. But it is more flexible, which makes it particularly suitable for vegetable gardens that are small or have irregular shaped beds.




